 Relevancy and Engagement
agclassroom.org/in/
Relevancy and Engagement
agclassroom.org/in/
Lesson Plan
Enlightened Concessions
Grade Level
Purpose
Through project-based learning, students conduct surveys with their peers at school about healthy food products they think will be marketable for school concessions. Based on surveys and research, they choose an in-demand product to test in class and then present to a guest panel as a healthy choice. Grades 6-8
Estimated Time
Materials Needed
Milestone 1: Entry Event
- Disposable eating supplies (plates, cups, spoons, napkins, etc.) to sample food
- Variety of food products prepared and displayed attractively for students to sample
- Snacks for Adults article
- New Food Label PowerPoint
- Food Label activity sheet
- Kids Health website
- Healthy Children website
Milestone 2: Research
- Computer, laptop, or tablet, Internet access, and/or recipe books and magazines
- Access to Google Forms
- List of available ingredients (teacher created)
- Calculators
- Online grocery website
Milestone 3: Product Testing
- Lab Job Duties and Assignments
- Revised group recipes
- Food supplies for each group's recipe
- Food preparation area (full kitchen area preferred)
- Device to take a picture
- Plates, napkins, spoons, cups, etc. for sampling food (disposable if needed to save time on the lab)
- Poster paper
- Sticky notes
Milestone 4: Final Product Presentation
- Computer and Internet access
- Pictures of food from lab
- Survey data
- Revised recipe
- Presentation Rubric
- Pencils or pens for guests
Vocabulary
6 essential nutrients: water, vitamins, minerals, fats/oils, carbohydrates, protein
added sugars: sugars such as sucrose (table sugar), corn syrups, and artificial sweeteners that are added to food to increase sweetness
budget: a written financial spending plan that has specific limits and amounts
demand: a consumer's willingness and ability to buy a product
fiber (dietary): isolated, non-digestible carbohydrates that have beneficial physiological effects in humans
food groups: categories of food that build a healthy diet: dairy, protein, vegetables, fruits, grains
protein: an essential nutrient responsible for building tissue, cells, and muscle
supply: how much of a good or service is available
time constraints: a specific amount of time in which to do something/work
unit cost: how much it will cost for an individual product (or specific unit of measurement)
whole grain: contains all three edible parts (the endosperm, bran, and germ) in the same proportions as the harvested grain seed before it is processed
Background Agricultural Connections
| Enlightened Concessions is a Project-Based Learning (PBL) plan. PBL is a teaching method in which students gain knowledge and skills by working for an extended period of time to investigate and respond to an authentic, engaging, and complex question, problem, or challenge.1 |
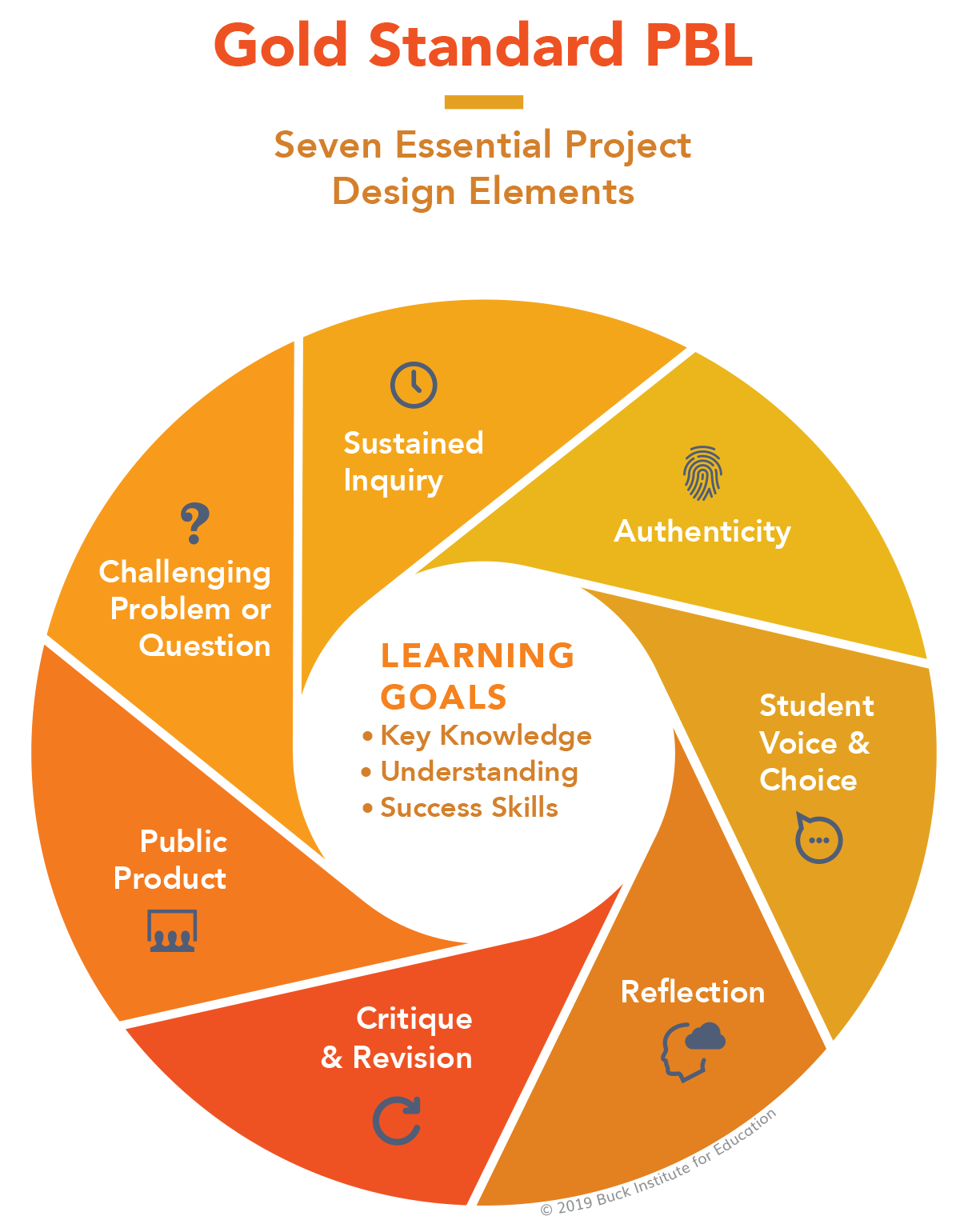
Essential Elements of PBL
A quality PBL experience requires seven essential elements.
- Challenging Problem or Question: The project is framed by a meaningful problem to be solved or a question to answer, at the appropriate level of challenge.
- Sustained Inquiry: Students engage in a rigorous, extended process of posing questions, finding resources, and applying information.
- Authenticity: The project involves real-world context, tasks and tools, quality standards, or impact, or the project speaks to personal concerns, interests, and issues in the students' lives.
- Voice and Choice: Students make some decisions about the project, including how they work and what they create.
- Reflection: Students and teachers reflect on the learning, the effectiveness of their inquiry and project activities, the quality of student work, and obstacles that arise and strategies for overcoming them.
- Critique and Revision: Students give, receive, and apply feedback to improve their process and products.
- Public Product: Students make their project work public by explaining, displaying, and/or presenting it to audiences beyond the classroom.2
Healthy Snacks
What makes a snack healthy may vary based on an individual's lifestyle and dietary needs, but general guidelines include:
- low in added sugars
- high in vitamins and minerals (10% daily value or higher in any specific one)
- high fiber (10% or more daily value)
- whole grains (at least half of all grains consumed in a day should be whole)
- high in protein (5g or more)
- includes more than one food group
- low in fat (<10% daily value)
- low calories (generally <200)
For this project, students require basic competency with common cooking abbreviations, terms, equivalents, nutrition, measuring techniques, basic math, safety, and sanitation. These concepts are typically easier to understand when students can see or experience them in action. Resources to teach measuring include:
- How to Measure Wet and Dry Ingredients
- How to Cut In Butter
- How to Knead Dough
- How to Fold Ingredients
- A Day in the Life of a Chef Student
Career HighlightsThis PBL plan introduces students to the following career opportunities: food scientist and technologist, dietitian and nutritionist, baker, food batchmaker, marketing specialist, graphic designer, general and operations manager, retail salesperson, customer service representative, advertising and promotions manager, advertising sales agent, chefs and head cooks, food service manager. Explore the career profiles to discover job outlooks, education requirements, and average salaries. |
Engage
At the beginning of the project, students are introduced to key content using a compelling situation that provides context and serves as a catalyst for an authentic problem or challenge. In Project-Based Learning (PBL), this authentic problem/challenge is referred to as an "Entry Event." Students use the Entry Event to initiate inquiry by reflecting on their prior knowledge of the key content, generating questions that they need to know the answers to in order to successfully complete the project or process that will solve the problem, and identifying what their next steps might be to answer their questions. These questions are used in an ongoing way throughout the project to track learning and guide inquiry.3 While students may have several questions, one driving question needs to be agreed upon that, when answered, should address the initial solution. Refer to Milestone 1 for Entry Event procedures.
Explore and Explain
In PBL, projects are organized into milestones. Each milestone represents a significant stage of the project. Click on each milestone below to access instructional procedures.
- Milestone 1: Entry Event (approximately 2 days)
- Milestone 2: Research (approximately 3 days)
- Milestone 3: Product Testing (approximately 3 days)
- Milestone 4: Final Product Presentation (approximately 3 days)