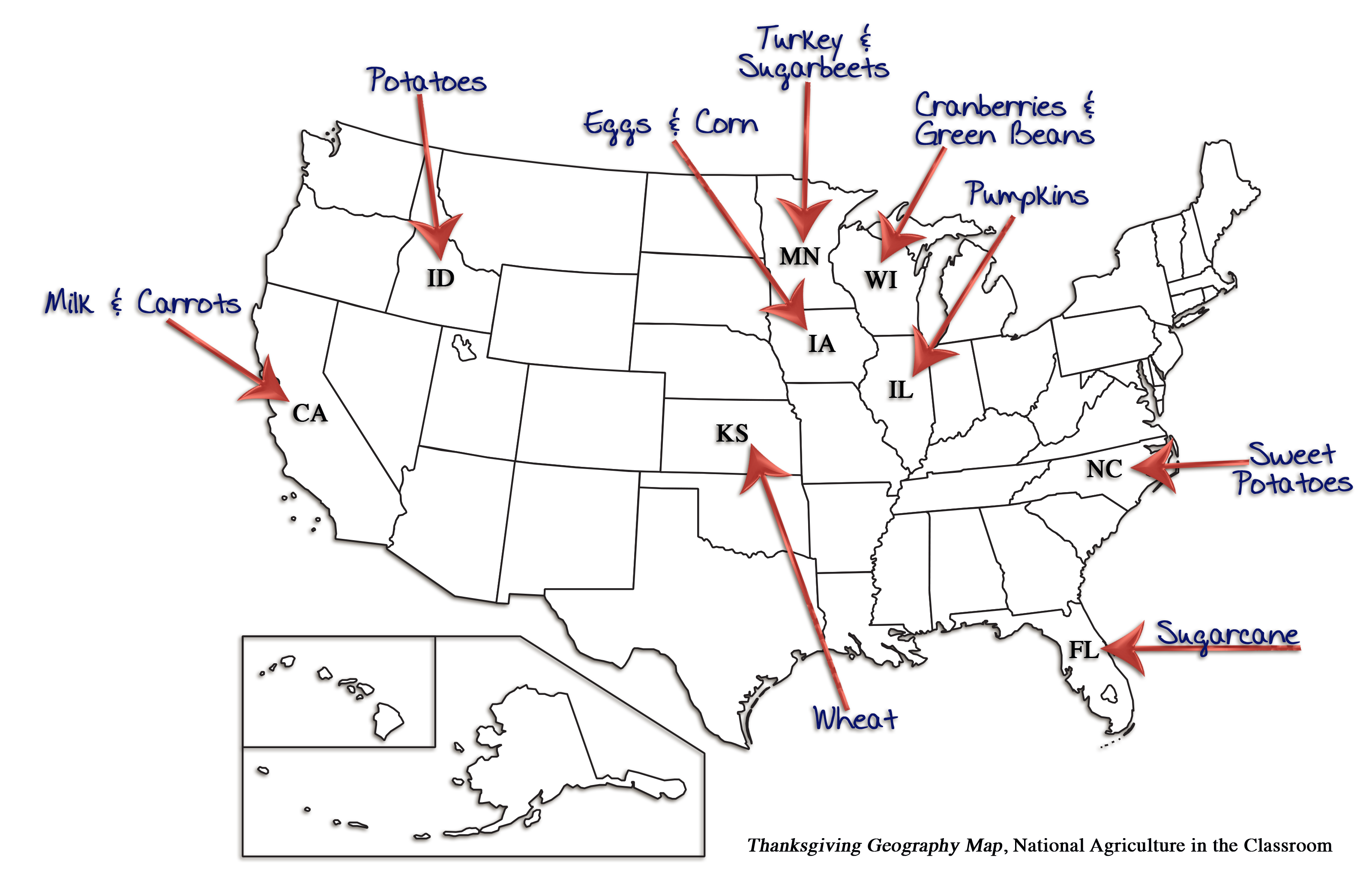
The Geography of Thanksgiving Dinner (Grades 6-8)
Identify common Thanksgiving foods and their farm source, determine if those foods can be produced locally, and locate the common origins of their Thanksgiving day dinner.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Andrea Gardner | National Agriculture in the Classroom Organization (NAITCO)
Sources
- http://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/in-the-news/pumpkins-background-statistics.aspx
- http://extension.illinois.edu/gardenerscorner/issue_02/fall_05_05.cfm
- http://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/animal-products/poultry-eggs/media-resources-turkey-market.aspx
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cranberry
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wheat_production_in_the_United_States
- http://www.nass.usda.gov/Charts_and_Maps/Poultry/eggmap.asp
- http://www.dairyfarmingtoday.org/Learn-More/FactsandFigures/Pages/StateStatistics.aspx
- http://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/crops/sugar-sweeteners/background.aspx
- http://www.ers.usda.gov/media/1834605/vgs-355-sa1.pdf
- http://www.nass.usda.gov/Statistics_by_State/Wisconsin/Publications/Crops/2013/vegannual.pdf
- http://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/crops/corn/background.aspx
- http://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/crops/vegetables-pulses/potatoes.aspx
- http://www.agmrc.org/commodities__products/vegetables/carrots/
Standards
Indiana Content Area Standards
-
Social Studies. Grade 8: Geography: Standard 3
Students identify the major geographic characteristics of the United States and its regions. They name and locate the major physical features of the United States, as well as demonstrate a broad understanding of the states, capitals and major cities, and use geographic skills and technology to examine the influence of geographic factors on national development.
- 8.3.2 Places and Regions: Read and interpret maps that portray the physical growth and development of the United States from colonization through Reconstruction (1877).
- 8.3.3 Physical Systems: Identify and locate the major climate regions in the United States and describe the characteristics of these regions.
- 8.3.5 Human Systems: Identify the agricultural regions of the United States and be able to give explanations for how the land was used and developed during the growth of the United States.
- 8.3.6 Human Systems: Using maps identify changes influenced by growth, economic development and human migration in the United States.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 6.RV.1
Acquire and use accurately grade-level appropriate general academic and content-specific words and phrases; gather vocabulary knowledge when considering a word or phrase important to comprehension or expression.
- Vocabulary in Literature and Nonfiction Texts.6.RV.3.2: Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a nonfiction text, including figurative, connotative, and technical meanings.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 6.W.1
Write routinely over a variety of time frames for a range of tasks, purposes, and audiences; apply reading standards to support analysis, reflection, and research by drawing evidence from literature and nonfiction texts.
- Writing Genres: Argumentative, Informative, and Narrative.6.W.3.2: Write informative compositions in a variety of forms that a. Introduce a topic; organize ideas, concepts, and information, using strategies such as definition and classification. b. Develop the topic with relevant facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples from various sources and texts. c. Use appropriate transitions to clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts. d. Include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., charts, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. e. Choose language and content specific vocabulary that express ideas precisely and concisely, recognizing and eliminating wordiness and redundancy. f. Establish and maintain a style appropriate to purpose and audience. g. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from the information or explanation presented.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 6.SL.1
Listen actively and adjust the use of spoken language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes.
- Discussion and Collaboration.6.SL.2.2: Elaborate and reflect on ideas under discussion by identifying specific evidence from materials under study and other resources.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 7.RV.1
Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate general academic and content-specific words and phrases; gather vocabulary knowledge when considering a word or phrase important to comprehension or expression.
- Vocabulary in Literature and Nonfiction Texts.7.RV.3.2: Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a nonfiction text, including figurative, connotative, and technical meanings; analyze the impact of a specific word choice on meaning and tone.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 7.W.1
Write routinely over a variety of time frames for a range of tasks, purposes, and audiences; apply reading standards to support analysis, reflection, and research by drawing evidence from literature and nonfiction texts.
- Writing Genres: Argumentative, Informative, and Narrative.7.W.3.2: Write informative compositions in a variety of forms that a. Introduce a topic clearly, previewing what is to follow; organize ideas, concepts, and information, using strategies such as definition and classification; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., charts, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. b. Develop the topic with relevant facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples from various sources and texts. c. Use appropriate transitions to create cohesion and clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts. d. Choose language and content-specific vocabulary that express ideas precisely and concisely, recognizing and eliminating wordiness and redundancy. e. Establishandmaintainastyleappropriatetopurposeandaudience. f. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 7.SL.1
Listen actively and adjust the use of spoken language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes.
- Discussion and Collaboration.7.SL.2.1: Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (e.g., one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) on grade- appropriate topics, texts, and issues, building on others ideas and expressing personal ideas clearly.
- Discussion and Collaboration.7.SL.2.2: Investigate and reflect on ideas under discussion by identifying specific evidence from materials under study and other resources.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 8.RV.1
Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate general academic and content-specific words and phrases; gather vocabulary knowledge when considering a word or phrase important to comprehension or expression.
- Vocabulary in Literature and Nonfiction Texts.8.RV.3.2: Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a nonfiction text, including figurative, connotative, and technical meanings; analyze the impact of specific word choices on meaning and tone, including analogies or allusions to other texts.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 8.W.1
Write routinely over a variety of time frames for a range of tasks, purposes, and audiences; apply reading standards to support analysis, reflection, and research by drawing evidence from literature and nonfiction texts.
- Writing Genres: Argumentative, Informative, and Narrative.8.W.3.2: Write informative compositions in a variety of forms that a. Introduce a topic clearly, previewing what is to follow; organize ideas, concepts, and information into broader categories; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., charts, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. b. Develop the topic with relevant, well-chosen facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples from various sources and texts. c. Use appropriate and varied transitions to create cohesion and clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts. d. Choose language and content-specific vocabulary that express ideas precisely and concisely, recognizing and eliminating wordiness and redundancy. e. Establishandmaintainastyleappropriatetothepurposeandaudience. f. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 8.SL.1
Listen actively and adjust the use of spoken language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes.
- Discussion and Collaboration.8.SL.2.1: Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (e.g., one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) on grade- appropriate topics, texts, and issues, building on others ideas and expressing personal ideas clearly.
- Discussion and Collaboration.8.SL.2.2: Examine, analyze, and reflect on ideas under discussion by identifying specific evidence from materials under study and other resources.
-
Social Studies. Grade 6: History: Standard 1
Students explore the key historic movements, events, and figures that contributed to the development of modern Europe and America from early civilizations through modern times by examining religious institutions, trade and cultural interactions, political institutions, and technological developments.
- 6.1.21 Chronological Thinking, Historical Comprehension, Analysis and Interpretation, Research: Form research questions and use a variety of information resources to obtain, evaluate and present data on people, cultures and developments in Europe and the Americas.
-
Social Studies. Grade 8: History: Standard 1
Students examine the relationship and significance of themes, concepts, and movements in the development of United States history, including the review of key ideas related to the colonization of America and the revolution and Founding Era. This will be followed by emphasis on social reform, national development and westward expansion, and the Civil War and Reconstruction period.
- 8.1.2 Historical Knowledge - American Revolution and Founding of the United States: 1754 to 1801: Compare and contrast reasons for British, French, Spanish and Dutch colonization in the New World.