Journey 2050 Lesson 1: Sustainable Agriculture (Grades 9-12)
Students will explore the question, “How will we sustainably feed nearly 10 billion people by the year 2050?” as they discover what sustainable agriculture is and how it is critical to securing a stable food supply and future for a growing population.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Lindsey Verhaeghe, Andrea Gardner, Debra Spielmaker, and Sara Hunt | National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL) and Nutrien
Acknowledgements
The Journey 2050 program was originally developed by Nutrien in collaboration with Calgary Stampede, Alberta Canola Producers Commission, Nutrients for Life Foundation, and Agriculture in the Classroom Canada. Authors and contributors were drawn from each of these organizations under the direction of Lindsey Verhaeghe (Nutrien) and Robyn Kurbel (Calgary Stampede.) The lessons were updated and revised in 2017 and 2022 with contributions from the original J2050 Steering Committee, the National Center for Agricultural Literacy, and the National Agriculture in the Classroom Organization.
Sources
- http://www.economist.com/node/18200702
- Sustainable Development Network Solutions (2013). Solutions for Sustainable Agriculture and Food Systems http://unsdsn.org/mwg-internal/de5fs23hu73ds/progress?id=EHV3NQH3C4-PP-EivDwXY4i2HzIjIWty8lBnkNioco0,
- http://www.fao.org/mwg-internal/de5fs23hu73ds/progress?id=HXecPI0p3XpJtFbAsjLRZd3G4ZjPgUW5N3PqtZYwwio
- http://waterfortheworld.net/index.php?id=12
- http://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/
- Sustainable Development Network Solutions (2013). Solutions for Sustainable Agriculture and Food Systems http://unsdsn.org/mwg-internal/de5fs23hu73ds/progress?id=EHV3NQH3C4-PP-EivDwXY4i2HzIjIWty8lBnkNioco0,
- https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/poverty/
- https://www.wfp.org/stories/5-facts-about-food-waste-and-hunger#:~:text=1, and http://www.un.org/waterforlifedecade/food_security.shtml
- https://irp-cdn.multiscreensite.com/be6d1d56/files/uploaded/TG07-Agriculture-Report-WEB.pdf
- http://www.economist.com/node/18200702
- http://www.worldfooddayusa.org/food_waste_the_facts
- http://www.un.org/en/globalissues/briefingpapers/population/vitalstats.shtml
- Sustainable Development Network Solutions (2013). Solutions for Sustainable Agriculture and Food Systems http://unsdsn.org/mwg-internal/de5fs23hu73ds/progress?id=EHV3NQH3C4-PP-EivDwXY4i2HzIjIWty8lBnkNioco0
Standards
Indiana Content Area Standards
-
Economics: Scarcity and Economic Reasoning; Standard 1
Students understand that productive resources are limited; therefore, people, institutions, and governments cannot have all the goods and services they want. As a result, people, institutions, and governments must choose some things and give up others.
- E.1.5 Scarcity and Economic Reasoning: Define scarcity and explain how choices incur opportunity costs and trade-offs.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 9-10.RV.1
Acquire and accurately use academic and content-specific words and phrases at the college and career readiness level; demonstrate independence in gathering vocabulary knowledge when considering a word or phrase important to comprehension or expression.
- Vocabulary in Literature and Nonfiction Texts.9-10.RV.3.2: Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a nonfiction text, including figurative, connotative, denotative, and technical meanings; evaluate the effectiveness of specific word choices on meaning and tone in multiple and varied contexts.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 9-10.SL.1
Listen actively and adjust the use of spoken language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes.
- Discussion and Collaboration.9-10.SL.2.1: Initiate and participate effectively in a range of collaborative discussions on grade-appropriate topics, texts, and issues, building on others ideas and expressing personal ideas clearly and persuasively.
- Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas.9-10.SL.4.2: Create engaging presentations that make strategic and creative use of digital media (e.g., textual, graphical, audio, visual, and interactive elements) to enhance audience understanding of findings, reasoning, and evidence.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 11-12.RV.1
Acquire and accurately use academic and content-specific words and phrases at the college and career readiness level; demonstrate independence in gathering vocabulary knowledge when considering a word or phrase important to comprehension or expression.
- Vocabulary in Literature and Nonfiction Texts.11-12.RV.3.2: Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a nonfiction text, including figurative, connotative, denotative, and technical meanings; evaluate the cumulative impact of how an author uses and refines the meaning of a key term or terms over the course of a text.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 11-12.SL.1
Listen actively and adjust the use of spoken language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes.
- Discussion and Collaboration.11-12.SL.2.1: Initiate and engage in a range of collaborative discussions on grade-appropriate topics, texts, and issues, building on others ideas and expressing personal ideas clearly and persuasively.
- Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas.11-12.SL.4.2: Create engaging presentations that make strategic and creative use of digital media (e.g., textual, graphical, audio, visual, and interactive elements) to add interest and enhance audience understanding of findings, reasoning, and evidence.
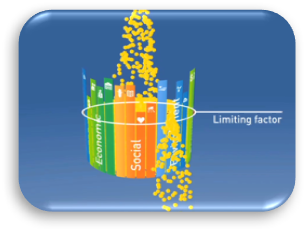 The economic component of sustainability is about earning money—creating jobs and incomes to support the national and local community. The social element encompasses things like food, education, medical care and infrastructure, including the roads used to transport food from the farm to your plate. And finally, there are environmental needs to consider. Soil quality needs to be maintained, habitats need protection, water must be conserved, and we need to protect our atmosphere by keeping greenhouse gas emissions to a minimum.
The economic component of sustainability is about earning money—creating jobs and incomes to support the national and local community. The social element encompasses things like food, education, medical care and infrastructure, including the roads used to transport food from the farm to your plate. And finally, there are environmental needs to consider. Soil quality needs to be maintained, habitats need protection, water must be conserved, and we need to protect our atmosphere by keeping greenhouse gas emissions to a minimum. Preparation: Prior to class, review the Background Information, video clip, and slide deck associated with the lesson. Review the
Preparation: Prior to class, review the Background Information, video clip, and slide deck associated with the lesson. Review the 