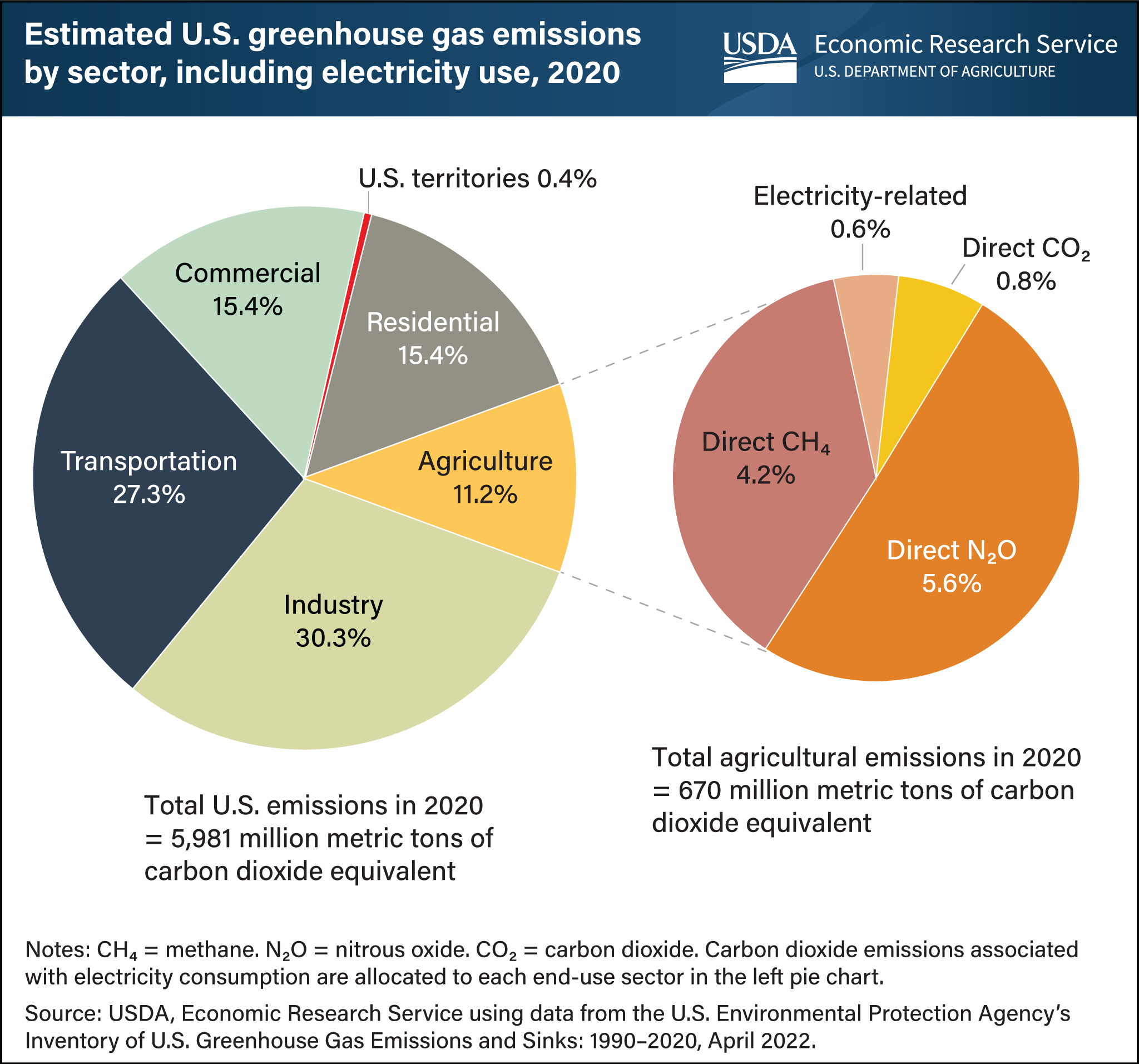
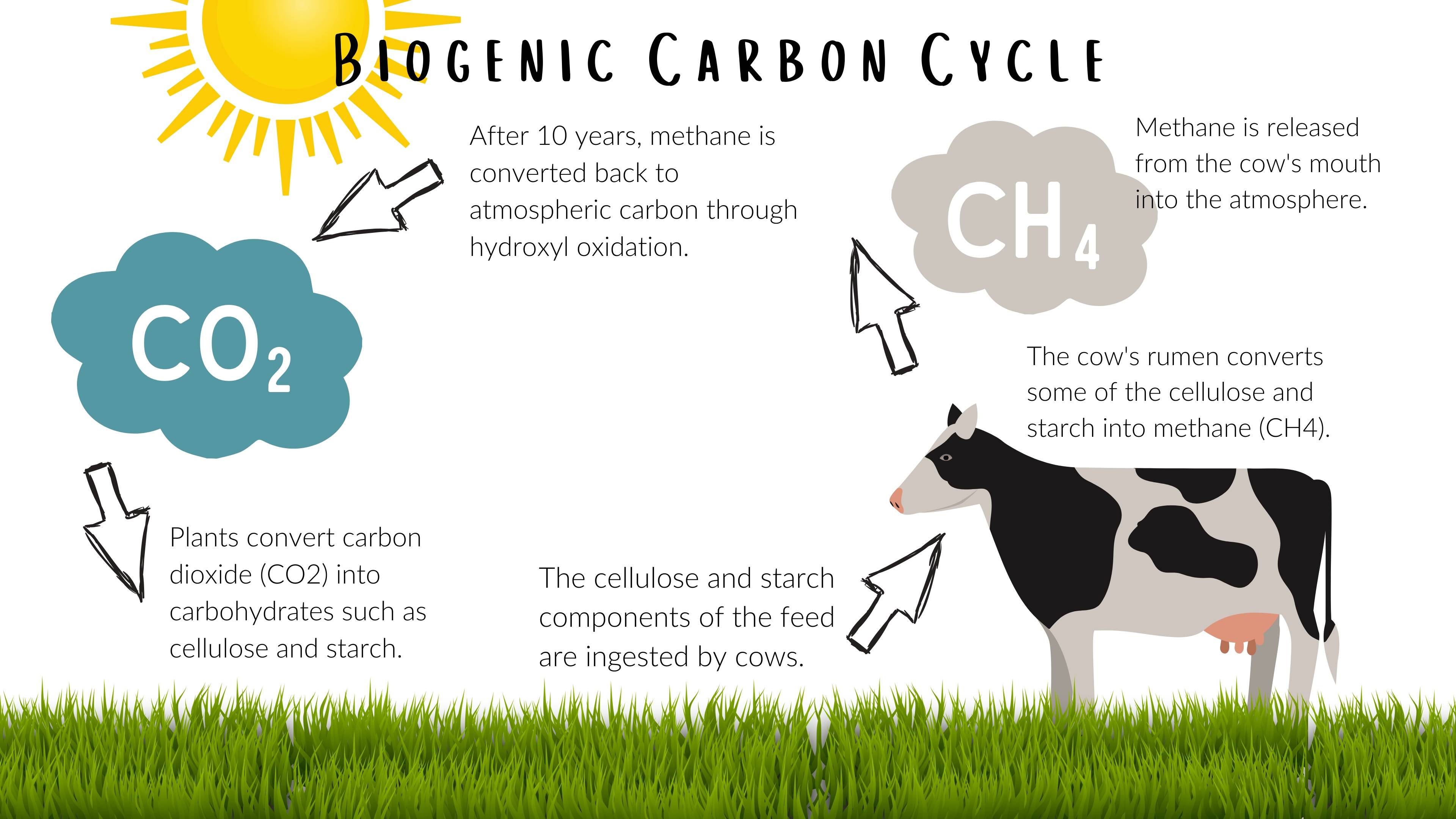
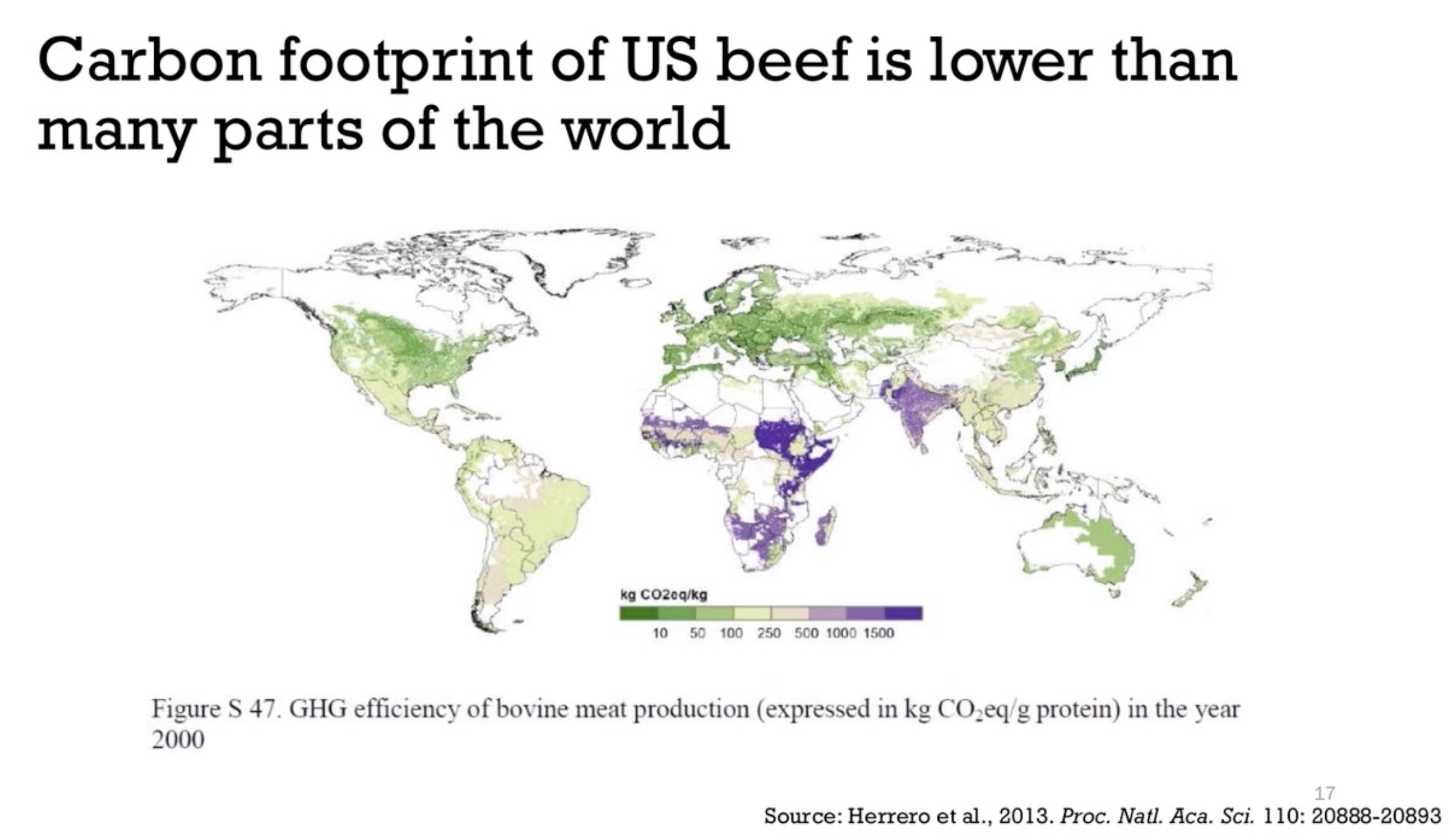
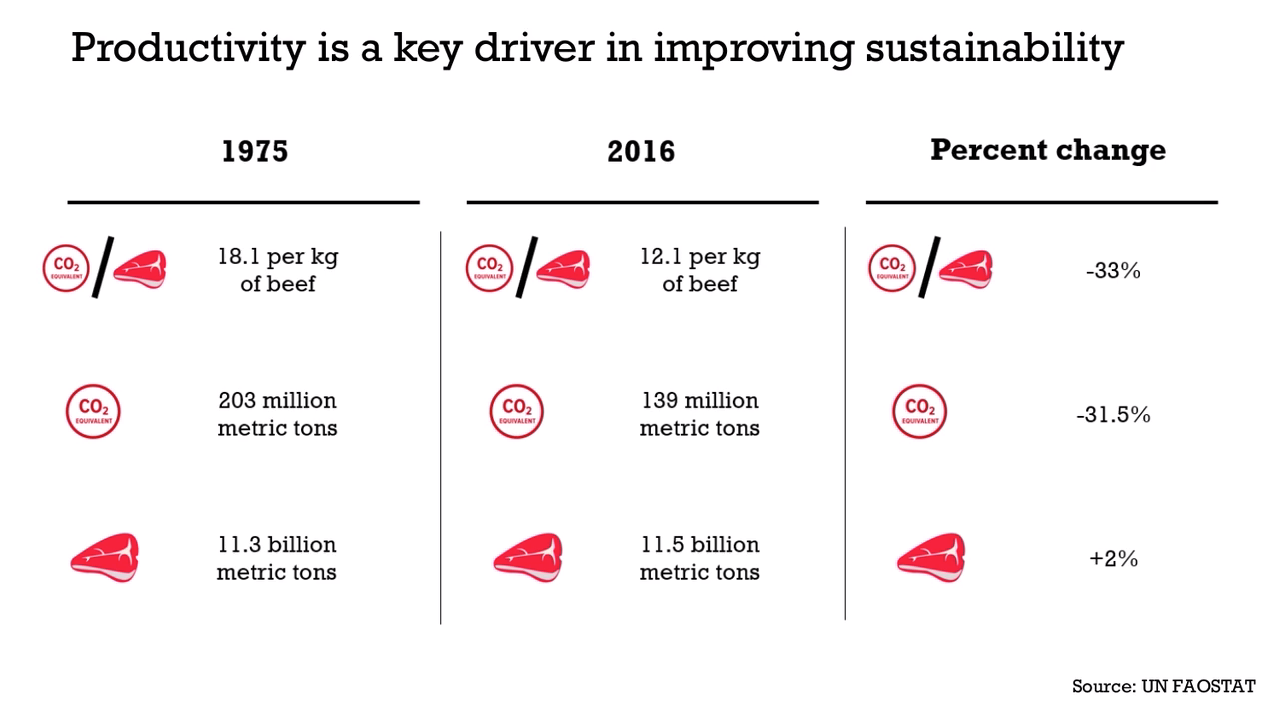
Carbon Hoofprints: Cows and Climate Change
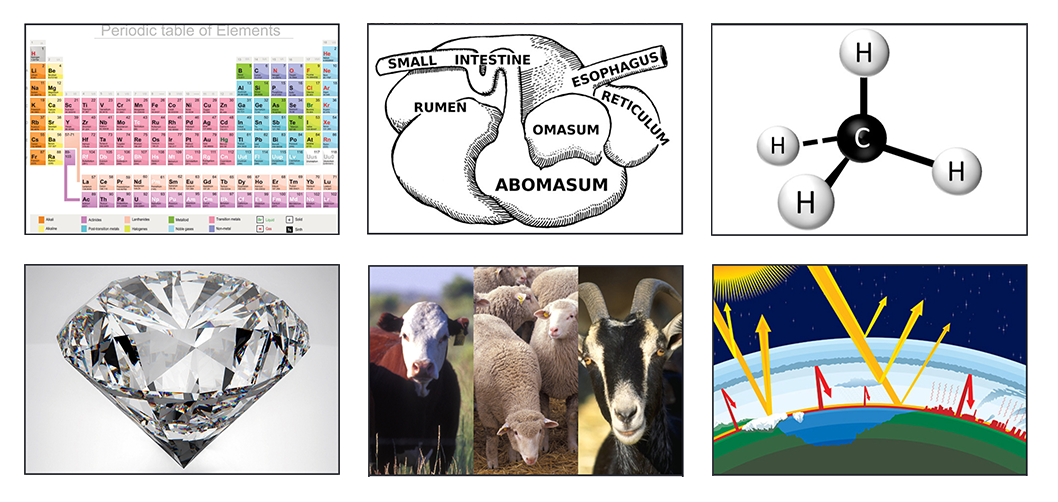
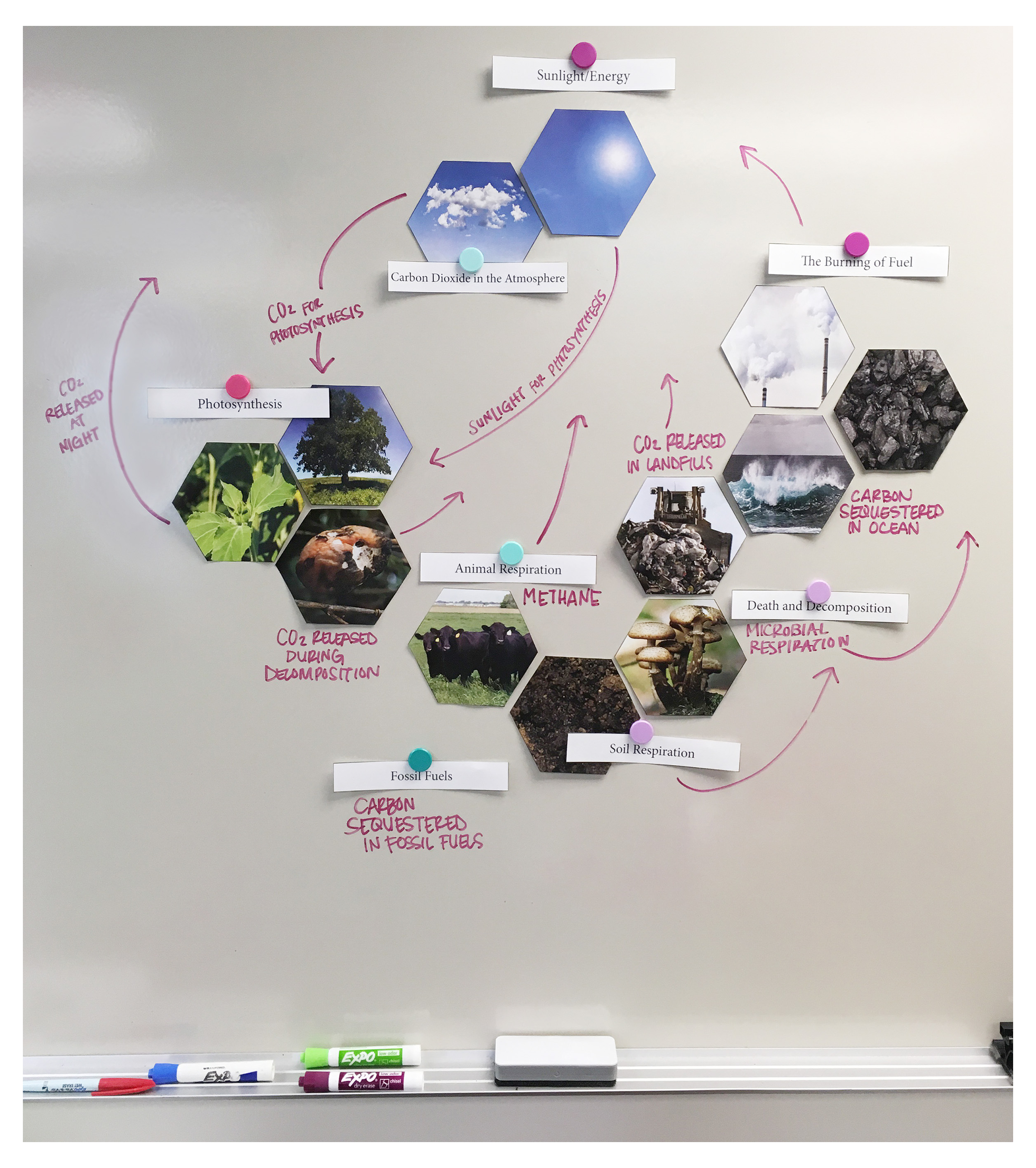
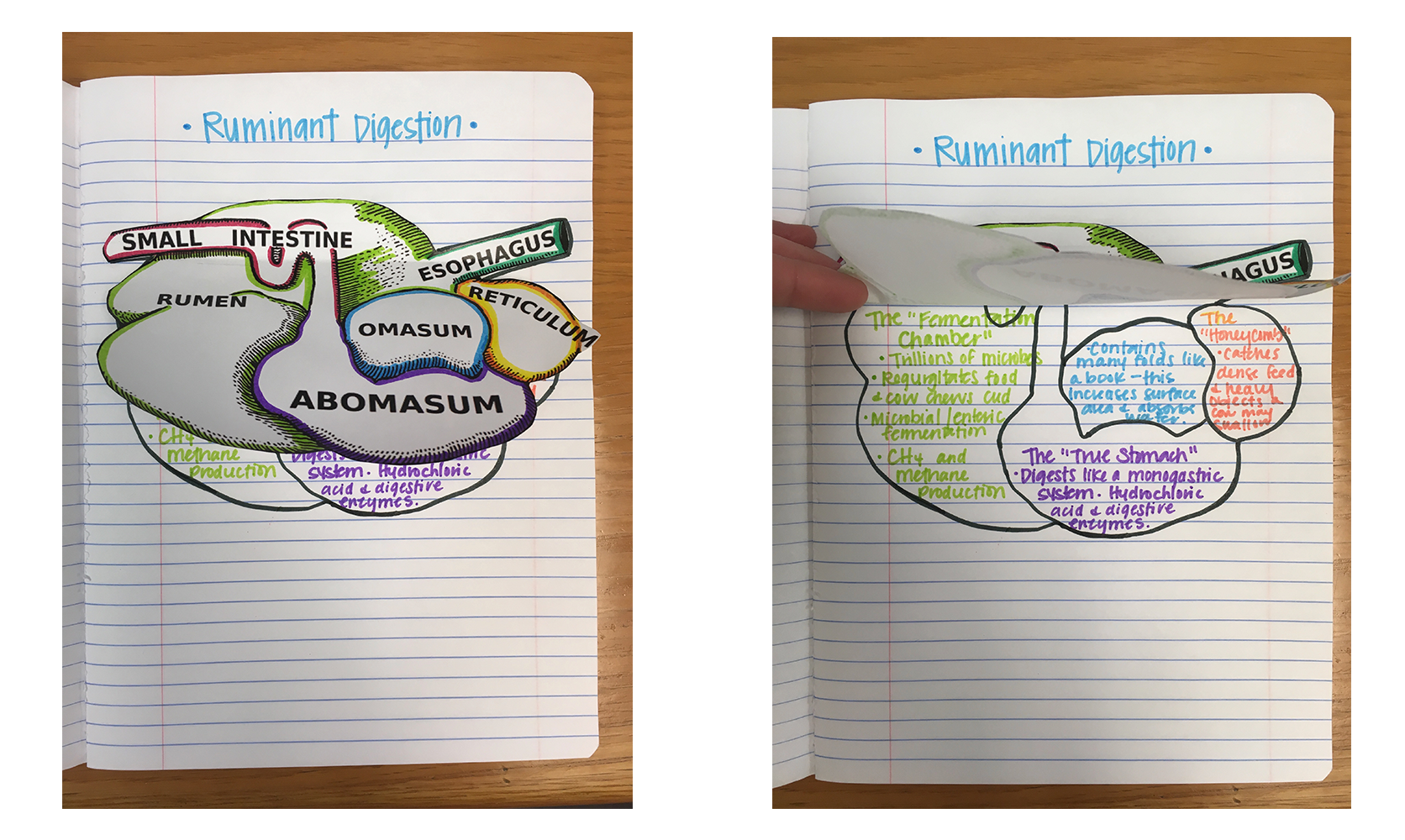
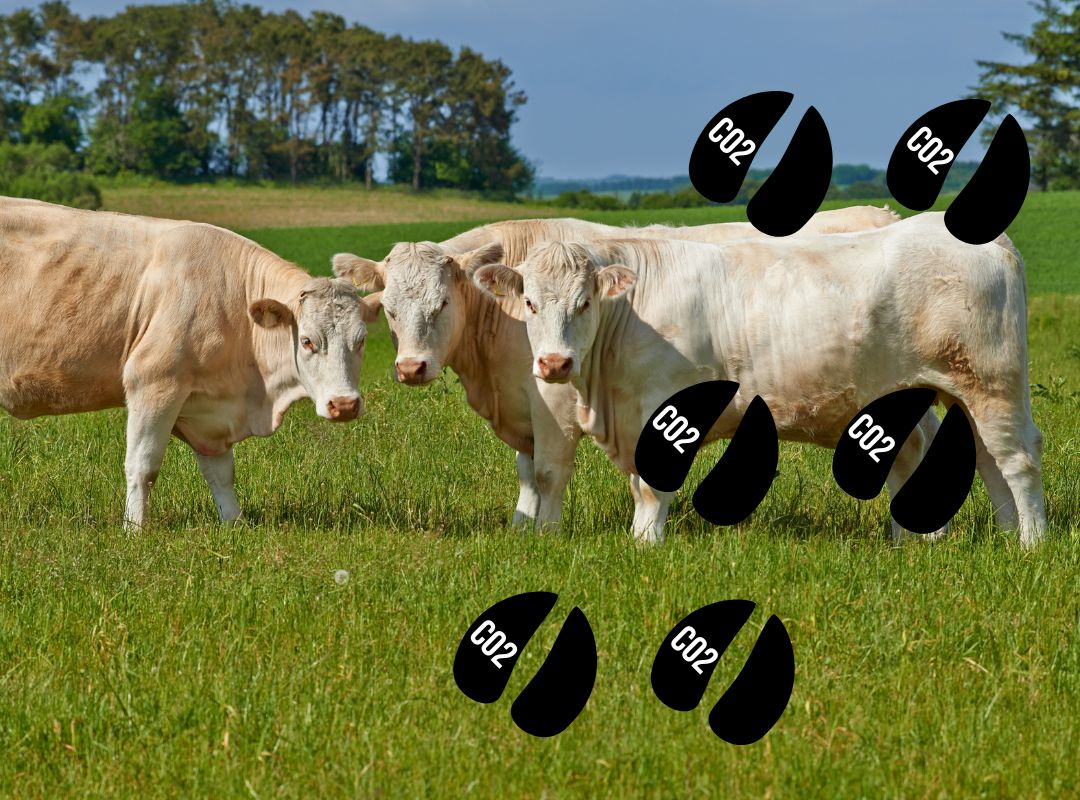
Students explore the carbon cycle and evaluate the carbon footprint of cattle. Using critical thinking skills, students will use the Claim, Evidence, and Reasoning model to determine the effect of cows’ methane production on the environment and investigate the extent cattle contribute to climate change.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Bekka Israelsen and Andrea Gardner | Utah Agriculture in the Classroom and National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL)
Sources
- https://caes.ucdavis.edu/news/articles/2016/04/livestock-and-climate-change-facts-and-fiction
- https://www.animalhealthmedia.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/Addressing-the-2050-food.pdf
- https://theconversation.com/yes-eating-meat-affects-the-environment-but-cows-are-not-killing-the-climate-94968
- https://castbox.fm/episode/099%3A-Frank-Mitloehner%3A-Cattle%2C-climate-change-and-the-methane-myth-id1016351-id166145089?country=us
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tfV0XwJSLrI
- http://pods.dasnr.okstate.edu/docushare/dsweb/Get/Document-10191/ANSI-3293.pdf
- https://www.dirt-to-dinner.com/grass-or-grain-beef-is-beef/
- https://kidsgardening.org/garden-how-to-carbon-cycle-and-carbon-sequestration/?utm_source=KidsGardening+Friends&utm_campaign=83eb3dba50-EMAIL_CAMPAIGN_2019_05_01_09_25&utm_medium=email&utm_term=0_0a82c9a42d-83eb3dba50-366559713&mc_cid=83eb3dba50&mc_eid=b1977826f2
- https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2019-04/documents/us-ghg-inventory-2019-main-text.pdf
- https://extension.umn.edu/dairy-nutrition/ruminant-digestive-system#stomach-compartments-1000460
- https://learningstore.uwex.edu/Assets/pdfs/A4131-01.pdf
- https://www3.epa.gov/climatechange//kids/index.html
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PR7ATkTXSb8&list=PLJEeYejb4pU_hRlOxpkNJ1EWELOAgIIeC
Standards
Indiana Content Area Standards
-
English Language Arts.Grade 9-10.RN.1
Read a variety of nonfiction within a range of complexity appropriate for grades 9-10. By the end of grade 9, students interact with texts proficiently and independently at the low end of the range and with scaffolding as needed for texts at the high end of the range. By the end of grade 10, students interact with texts proficiently and independently.
- Key Ideas and Textual Support.9-10.RN.2.1: Analyze what a text says explicitly as well as inferences and interpretations drawn from the text by citing strong and thorough textual evidence.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 9-10.W.1
Write routinely over a variety of time frames for a range of tasks, purposes, and audiences; apply reading standards to support analysis, reflection, and research by drawing evidence from literature and nonfiction texts.
- Writing Genres: Argumentative, Informative and Narrative.9-10.W.3.2: Write informative compositions on a variety of topics that a. Introduce a topic; organize complex ideas, concepts, and information to make important connections and distinctions b. Developthetopicutilizingcrediblesourceswithrelevant,andsufficientfacts,extendeddefinitions,concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples appropriate to the audiences knowledge of the topic. c. Use appropriate transitions to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the relationships among complex ideas and concepts. d. Choose language and content-specific vocabulary that express ideas precisely and concisely to manage the complexity of the topic, recognizing and eliminating wordiness and redundancy. e. Establishandmaintainastyleappropriatetothepurposeandaudience. f. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented (e.g., articulating implications or the significance of the topic).
- Writing Genres: Argumentative, Informative, and Narrative.9-10.W.3.1: Write arguments in a variety of forms that: a. Introduceclaim(s),distinguishtheclaim(s)fromalternateoropposingclaims,andcreateanorganizationthat establishes clear relationships among claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence. b. Use rhetorical strategies to enhance the effectiveness of the claim c. Develop claim(s) and counterclaims fairly, supplying evidence for each while pointing out the strengths and limitations of both in a manner that anticipates the audiences knowledge level and concerns. d. Use effective transitions to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the relationships between claim(s) and reasons, between reasons and evidence, and between claim(s) and counterclaims. e. Establishandmaintainaconsistentstyleandtoneappropriatetopurposeandaudience. f. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the argument presented.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 9-10.SL.1
Listen actively and adjust the use of spoken language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes.
- Discussion and Collaboration.9-10.SL.2.1: Initiate and participate effectively in a range of collaborative discussions on grade-appropriate topics, texts, and issues, building on others ideas and expressing personal ideas clearly and persuasively.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 11-12.RN.1
Read a variety of nonfiction within a range of complexity appropriate for grades11-CCR. By the end of grade 11, students interact with texts proficiently and independently at the low end of the range and with scaffolding as needed for texts at the high end of the range. By the end of grade 12, students interact with texts proficiently and independently.
- Key Ideas and Textual Support.11-12.RN.2.1: Analyze what a text says explicitly as well as inferences and interpretations drawn from the text by citing strong and thorough textual evidence to support and explain how the evidence develops the analysis.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 11-12.W.1
Write routinely over a variety of time frames for a range of tasks, purposes, and audiences; apply reading standards to support analysis, reflection, and research by drawing evidence from literature and nonfiction texts.
- Writing Genres: Argumentative, Informative, and Narrative.11-12.W.3.1: Write arguments in a variety of forms that a. Introduce precise claim(s), establish the significance of the claim(s), distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and create an organization that logically sequences claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence. b. Use rhetorical strategies to enhance the effectiveness of the claim c. Develop claim(s) and counterclaims fairly and thoroughly, supplying the most relevant evidence for each while pointing out the strengths and limitations of both in a manner that anticipates the audiences knowledge level, concerns, values, and possible biases. d. Use effective and varied transitions as well as varied syntax to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the relationships between claim(s) and reasons, between reasons and evidence, and between claim(s) and counterclaims. e. Establishandmaintainaconsistentstyleandtoneappropriatetopurposeandaudience. f. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the argument presented.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 11-12.SL.1
Listen actively and adjust the use of spoken language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes.
- Discussion and Collaboration.11-12.SL.2.1: Initiate and engage in a range of collaborative discussions on grade-appropriate topics, texts, and issues, building on others ideas and expressing personal ideas clearly and persuasively.