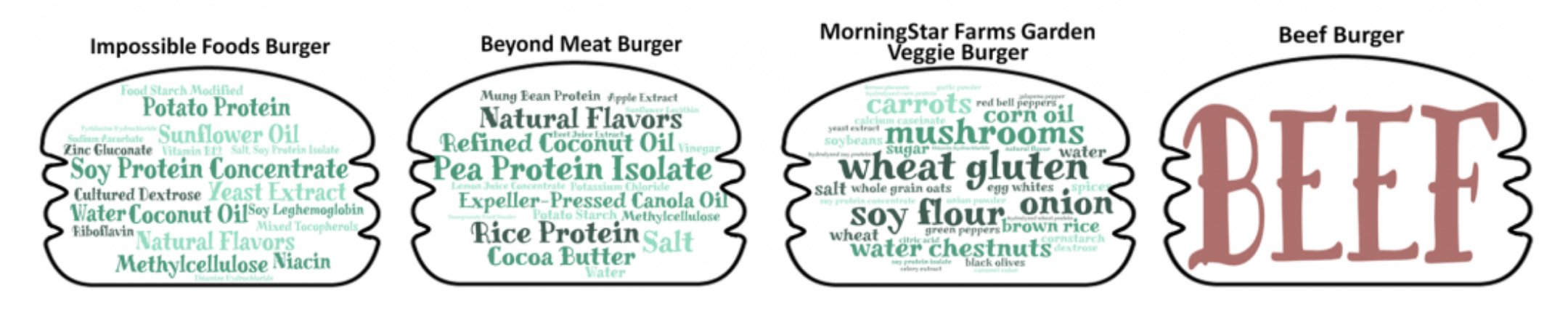
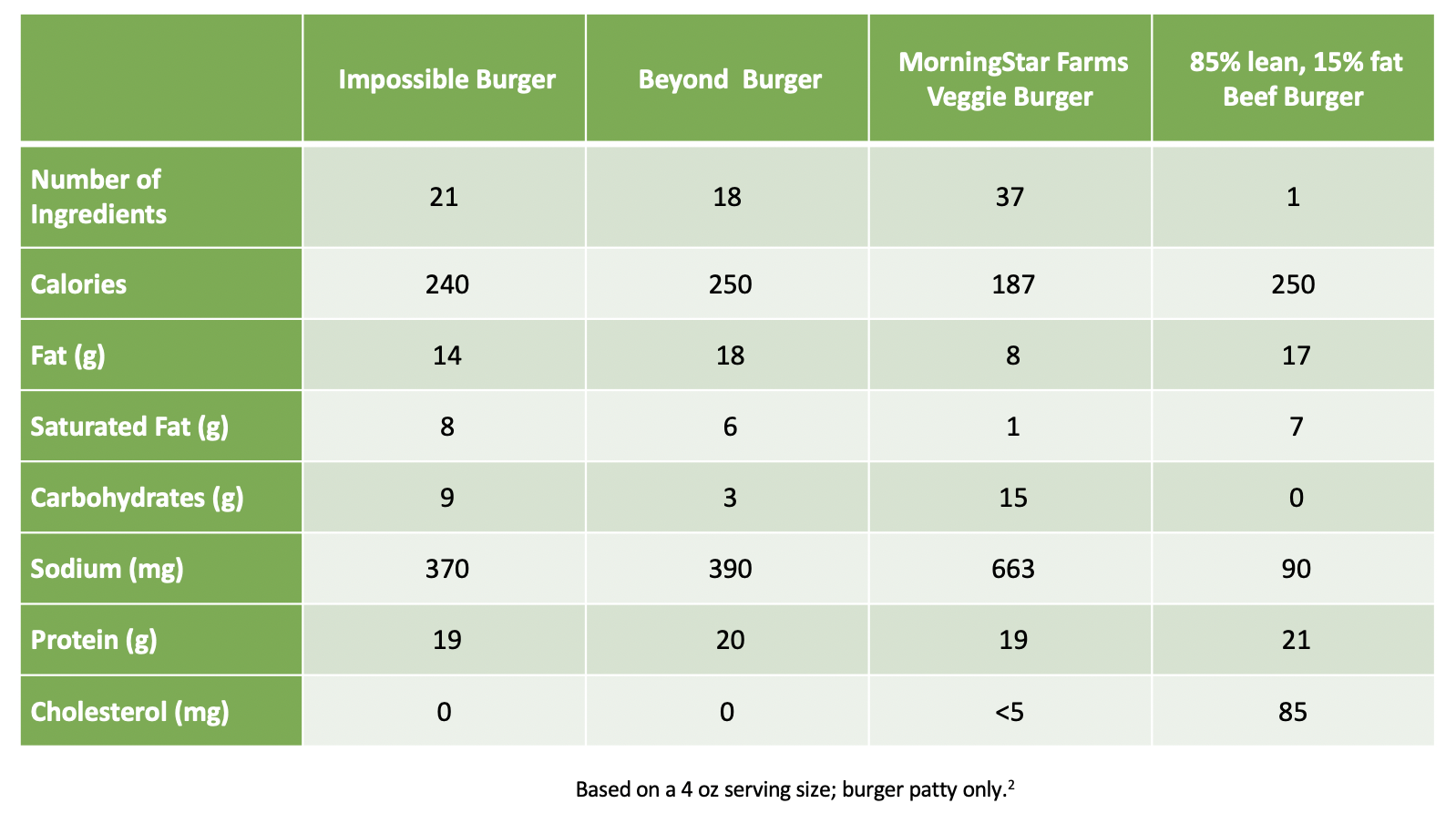
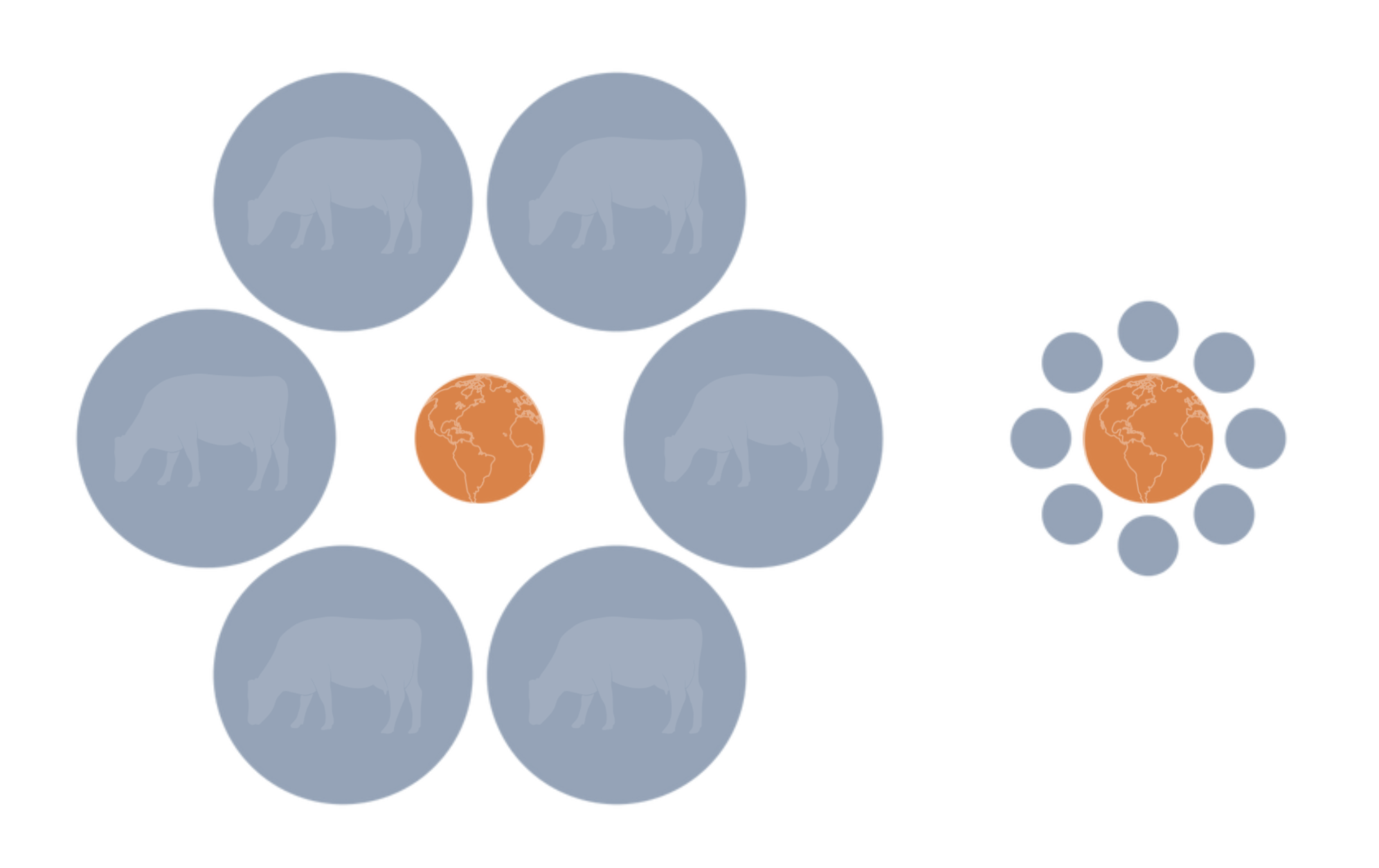
A Tale of Two Burgers: Beef and Plant-based Protein
Students compare the components of beef and plant-based burgers by determining the production and processing methods of each product; evaluate the ingredients and nutritional differences between beef and plant-based products; and discuss different points of view in the agricultural industry concerning plant-based proteins and traditional beef. This lesson covers a socioscientific issue and aims to provide students with tools to evaluate science within the context of social and economic points of view.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Bekka Israelsen | Utah Agriculture in the Classroom
Sources
- What's in a Name? In This Case, Quite a Bit | Dirt to Dinner
- Comparing Traditional & Alternative Burgers | Dirt to Dinner
- Home | Meat Institute
- Is a Plant-Based Diet Better for You? | Dirt to Dinner
- How Much Meat to Expect From a Beef Carcass PB1822.pdf | University of Tennessee Extension
- Impossible Foods Media Kit | Impossible Foods
- Impossible Foods
- Beyond Burger | Vegan Burger Patties | Beyond Meat
- July 4th Hot Dog and Hamburger Consumption by State | USA Today
- The History of the Veggie Burger | Smithsonian Magazine
- How do you make heme? | Impossible Foods
- What are the ingredients in Impossible™ Beef Meat From Plants? | Impossible Foods
- What are the nutrition facts for Impossible™ Beef Meat From Plants? | Impossible Foods
- Great Value Beef Burgers 85% Lean/15% Fat, 12ct, 3 lb (Frozen) | Walmart
Standards
Indiana Content Area Standards
-
Health and Wellness: Standard 2
Students will analyze the influence of family, peers, culture, media, technology, and other factors on health behaviors.
- 12.2.3 Health and Wellness: Evaluate the effect of media on health behaviors.
-
Health and Wellness: Standard 5
Students will demonstrate the ability to use decision-making skills to enhance health.
- 12.5.6 Health and Wellness: Assume responsibility for personal health decisions.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 9-10.W.1
Write routinely over a variety of time frames for a range of tasks, purposes, and audiences; apply reading standards to support analysis, reflection, and research by drawing evidence from literature and nonfiction texts.
- Writing Genres: Argumentative, Informative and Narrative.9-10.W.3.2: Write informative compositions on a variety of topics that a. Introduce a topic; organize complex ideas, concepts, and information to make important connections and distinctions b. Developthetopicutilizingcrediblesourceswithrelevant,andsufficientfacts,extendeddefinitions,concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples appropriate to the audiences knowledge of the topic. c. Use appropriate transitions to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the relationships among complex ideas and concepts. d. Choose language and content-specific vocabulary that express ideas precisely and concisely to manage the complexity of the topic, recognizing and eliminating wordiness and redundancy. e. Establishandmaintainastyleappropriatetothepurposeandaudience. f. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented (e.g., articulating implications or the significance of the topic).
-
English Language Arts.Grade 9-10.SL.1
Listen actively and adjust the use of spoken language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes.
- Discussion and Collaboration.9-10.SL.2.1: Initiate and participate effectively in a range of collaborative discussions on grade-appropriate topics, texts, and issues, building on others ideas and expressing personal ideas clearly and persuasively.
- Discussion and Collaboration.9-10.SL.2.5: Respond thoughtfully to multiple perspectives, summarize points of agreement and disagreement, and, when warranted, qualify or justify personal views and understanding and make new connections in reference to the evidence and reasoning presented.
- Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas.9-10.SL.4.2: Create engaging presentations that make strategic and creative use of digital media (e.g., textual, graphical, audio, visual, and interactive elements) to enhance audience understanding of findings, reasoning, and evidence.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 9-10.ML.1
Critically analyze information found in a variety of mediums used to persuade, inform, entertain, and transmit culture.
- Media Literacy.9-10.ML.2.2: Analyze and interpret the changing role of the media in focusing the public's attention on events and informing their opinions on issues.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 11-12.W.1
Write routinely over a variety of time frames for a range of tasks, purposes, and audiences; apply reading standards to support analysis, reflection, and research by drawing evidence from literature and nonfiction texts.
- Writing Genres: Argumentative, Informative, and Narrative.11-12.W.3.2: Write informative compositions on a variety of topics that a. Introduce a topic; organize complex ideas, concepts, and information so that each new element builds on that which precedes it to create a unified whole;include formatting(e.g., headings), graphics (e.g.,figures,tables),and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. b. Utilizing credible sources, develop the topic thoroughly by selecting the most significant and relevant facts, extended definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples appropriate to the audiences knowledge of the topic c. Use appropriate and varied transitions and syntax to link the major sections of the text,create cohesion, and clarify the relationships among complex ideas and concepts. d. Choose language, content- specific vocabulary, and techniques to manage the complexity of the topic, recognizing and eliminating wordiness and redundancy. e. Establishandmaintainastyleappropriatetothepurposeandaudience. f. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented (e.g., articulating implications or the significance of the topic).
-
English Language Arts.Grade 11-12.SL.1
Listen actively and adjust the use of spoken language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes.
- Discussion and Collaboration.11-12.SL.2.1: Initiate and engage in a range of collaborative discussions on grade-appropriate topics, texts, and issues, building on others ideas and expressing personal ideas clearly and persuasively.
- Discussion and Collaboration.11-12.SL.2.5: Conduct, debate, and discuss to allow all views to be presented; allow for a dissenting view, in addition to group compromise; and determine what additional information or research is required to deepen the investigation or complete the task.
- Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas.11-12.SL.4.2: Create engaging presentations that make strategic and creative use of digital media (e.g., textual, graphical, audio, visual, and interactive elements) to add interest and enhance audience understanding of findings, reasoning, and evidence.
-
English Language Arts.Grade 11-12.ML.1
Critically analyze information found in electronic, print, and mass media used to entertain and transmit culture.
- Media Literacy.11-12.ML.2.2: Analyze the impact of the media on the public, including identifying and analyzing rhetorical and logical fallacies.